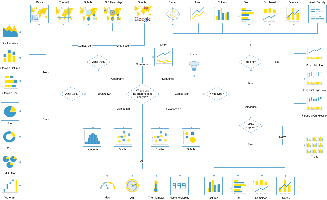
Overview
The first step in creating your chart is selecting the appropriate chart type to most effectively visualise your data. The following table of chart choices will assist you to make you selection.
One of the features of Yellowfin is that even after you have made a selection it is easy to swap between chart types to see how your data might look with different visualisations.
Type
Icon
When to Use
Area

You want to emphasize the magnitude of change over time. Use an area chart to show how much the value of a measure changes over time.
Stacked Area

You want to emphasise the magnitude of change over time, while comparing multiple categories.
Type |
Icon |
When to Use |
|---|---|---|
Area |
|
You want to emphasize the magnitude of change over time. Use an area chart to show how much the value of a measure changes over time. |
Stacked Area |
|
You want to emphasise the magnitude of change over time, while comparing multiple categories. |
Type
Icon
When to Use
Horizontal Bar

You want to highlight values for easy comparison and plot your numbers horizontally. Use a bar chart to place less emphasis on time and focus on comparing values.
3D Horizontal Bar
Similar to the horizontal bar chart, but in three a dimensional form.
Stacked Horizontal Bar

Categorical data, grouped or stacked to assist comparison. Use when part-to-whole comparison is important.
Horizontal Cylinder

Similar to the horizontal bar, but having chart components shown in cylindrical form.
Proportional Bar

Displays how close values in different categories came to the highest category value.
Type |
Icon |
When to Use |
|---|---|---|
Horizontal Bar |
|
You want to highlight values for easy comparison and plot your numbers horizontally. Use a bar chart to place less emphasis on time and focus on comparing values. |
3D Horizontal Bar |
|
Similar to the horizontal bar chart, but in three a dimensional form. |
Stacked Horizontal Bar |
|
Categorical data, grouped or stacked to assist comparison. Use when part-to-whole comparison is important. |
Horizontal Cylinder |
|
Similar to the horizontal bar, but having chart components shown in cylindrical form. |
Proportional Bar |
|
Displays how close values in different categories came to the highest category value. |
Type
Icon
When to Use
Vertical Column

You want to highlight values for easy comparison and plot your numbers vertically. Use a column chart to place less emphasis on time and focus on comparing values.
3D Vertical Bar

Similar to the vertical bar chart, but in three dimensional form.
Stacked Vertical Bar

Also referred to as stacked column charts and used when part-to-whole comparison is important.
Cylinder

Similar to the vertical bar, but having chart components shown in cylindrical form.
3D Stacked Vertical Bar

Similar to the 3d stacked vertical bar chart, but in three dimensional form.
Layered

Compares the contribution of each value to a total across categories.
Type |
Icon |
When to Use |
|---|---|---|
Vertical Column |
|
You want to highlight values for easy comparison and plot your numbers vertically. Use a column chart to place less emphasis on time and focus on comparing values. |
3D Vertical Bar |
|
Similar to the vertical bar chart, but in three dimensional form. |
Stacked Vertical Bar |
|
Also referred to as stacked column charts and used when part-to-whole comparison is important. |
Cylinder |
|
Similar to the vertical bar, but having chart components shown in cylindrical form. |
3D Stacked Vertical Bar |
|
Similar to the 3d stacked vertical bar chart, but in three dimensional form. |
Layered |
|
Compares the contribution of each value to a total across categories. |
Type
Icon
When to Use
Combination Charts

Combination charts, in effect, superimpose one chart type above or below another. Use to improve clarity and highlight relationships between data sets.
Overlay Chart

Use the line chart to emphasize a trend and bars to emphasize specific values. Line/Bar combinations may work better by de-emphasizing bars through the use of subtle colours.
Type |
Icon |
When to Use |
|---|---|---|
Combination Charts |
|
Combination charts, in effect, superimpose one chart type above or below another. Use to improve clarity and highlight relationships between data sets. |
Overlay Chart |
|
Use the line chart to emphasize a trend and bars to emphasize specific values. Line/Bar combinations may work better by de-emphasizing bars through the use of subtle colours. |
Type
Icon
When to Use
Financial Line

Use this chart to display a trading value with a subchart displaying volume.
High Low

Shows daily high, low, opening and closing values with tick positions corresponding to opening and closing values.
Candlestick
Shows daily high, low, opening and closing values with different colour bars depending on the daily direction.
Type |
Icon |
When to Use |
|---|---|---|
Financial Line |
|
Use this chart to display a trading value with a subchart displaying volume. |
High Low |
|
Shows daily high, low, opening and closing values with tick positions corresponding to opening and closing values. |
Candlestick |
|
Shows daily high, low, opening and closing values with different colour bars depending on the daily direction. |
Type
Icon
When to Use
Line

You want to view trends over time by plotting data at points connected by lines. Use a line chart to plot many metrics.
3D Line

Similar to the line chart, but in three-dimensional form.
Z Chart

Trends over a short period of time; displaying the data, accumulative total, and moving total.
Stepped Line

A line chart where movement is shown in steps rather than straight lines.
Type |
Icon |
When to Use |
|---|---|---|
Line |
|
You want to view trends over time by plotting data at points connected by lines. Use a line chart to plot many metrics. |
3D Line |
|
Similar to the line chart, but in three-dimensional form. |
Z Chart |
|
Trends over a short period of time; displaying the data, accumulative total, and moving total. |
Stepped Line |
|
A line chart where movement is shown in steps rather than straight lines. |
Type
Icon
When to Use
Image Maps

If you do not have GIS defined columns you can use the Image Maps to create heat maps - these are a good way to display metrics with a spatial element such as Revenue by State or Country
You will only be able to render maps for which an image map has been defined.
Google Maps

Google Maps allow you to render location data points onto a Google map which will be displayed as a Yellowfin Chart - along with associated Google map widgets.
You will have to have a Google Map Key to use this type of chart
GIS Maps
GIS Maps allow the rendering of complex GIS polygons. These can be used to render spatial reports on the fly based on the GIS data available in a report.
GIS Bubble Map

A bubble map in which bubble positions are specified by GIS points.
GIS Heat Map

A heat map where colours representing GIS points are blended based on intensity.
Type |
Icon |
When to Use |
|---|---|---|
Image Maps |
|
If you do not have GIS defined columns you can use the Image Maps to create heat maps - these are a good way to display metrics with a spatial element such as Revenue by State or Country |
Google Maps |
|
Google Maps allow you to render location data points onto a Google map which will be displayed as a Yellowfin Chart - along with associated Google map widgets. |
GIS Maps |
|
GIS Maps allow the rendering of complex GIS polygons. These can be used to render spatial reports on the fly based on the GIS data available in a report. |
GIS Bubble Map |
|
A bubble map in which bubble positions are specified by GIS points. |
GIS Heat Map |
|
A heat map where colours representing GIS points are blended based on intensity. |
Type
Icon
When to Use
Meter

You want to measure the rate of change of a measure against pre-defined targets. Useful for dashboard reporting.
Thermometer

Vertical representation of the meter chart, indicating a range of qualitative indicators.
Dial

Used to communicate key performance indicators.
Numeric Display

Shows the value of a metric on a digital display.
Type |
Icon |
When to Use |
|---|---|---|
Meter |
|
You want to measure the rate of change of a measure against pre-defined targets. Useful for dashboard reporting. |
Thermometer |
|
Vertical representation of the meter chart, indicating a range of qualitative indicators. |
Dial |
|
Used to communicate key performance indicators. |
Numeric Display |
|
Shows the value of a metric on a digital display. |
Type
Icon
When to Use
Pie

You want to show the relationship of parts to the whole. Use a pie chart to highlight proportions rather than actual values. If it is important to show actual values in the chart, avoid using the pie chart type.
3D Pie

Similar to the pie chart, but in three a dimensional form.
Multi Pie

Used to highlight individual component sizes in a system of multiple components.
Ring

Similar to the pie chart, but in a circular ring form.
Type |
Icon |
When to Use |
|---|---|---|
Pie |
|
You want to show the relationship of parts to the whole. Use a pie chart to highlight proportions rather than actual values. If it is important to show actual values in the chart, avoid using the pie chart type. |
3D Pie |
|
Similar to the pie chart, but in three a dimensional form. |
Multi Pie |
|
Used to highlight individual component sizes in a system of multiple components. |
Ring |
|
Similar to the pie chart, but in a circular ring form. |
Type
Icon
When to Use
Funnel
Used to show the status of stages in a process.
Radar
You want to compare data by integrating multiple axes into a single radial figure.
Waterfall

Waterfall charts are a special type of Floating Column Chart. A typical waterfall chart shows how an initial value is increased and decreased by a series of intermediate values, leading to a final value.
Event

Maps the occurrence of events against the values of a numeric data set over time.
Week Density

Shows the density of occurrences based on hour relative to other densities on the same day of the week.
Trellis

A segmented chart for which the behaviour is determined by the data selected.
Type |
Icon |
When to Use |
|---|---|---|
Funnel |
|
Used to show the status of stages in a process. |
Radar |
|
You want to compare data by integrating multiple axes into a single radial figure. |
Waterfall |
|
Waterfall charts are a special type of Floating Column Chart. A typical waterfall chart shows how an initial value is increased and decreased by a series of intermediate values, leading to a final value. |
Event |
|
Maps the occurrence of events against the values of a numeric data set over time. |
Week Density |
|
Shows the density of occurrences based on hour relative to other densities on the same day of the week. |
Trellis |
|
A segmented chart for which the behaviour is determined by the data selected. |
Type
Icon
When to Use
Bubble

Can be used with categorical, sequential or time-series data. Bubble size and location combine to effectively display 3-D data on a 2-D chart. Bubble charts can also be displayed in quadrants, allowing for negative X and Y values.
Scatter

A scatter plot (points not joined) chart that allows the charting of 2 related attribute series. Can only be used if the data series are related. Useful for seeing trends in data that is not linear.
Histogram
Shows the number of times a given value occurs in the dataset.
Box & Whisker
A chart which gives a quick overview of series of values and their statistical properties.
Type |
Icon |
When to Use |
|---|---|---|
Bubble |
|
Can be used with categorical, sequential or time-series data. Bubble size and location combine to effectively display 3-D data on a 2-D chart. Bubble charts can also be displayed in quadrants, allowing for negative X and Y values. |
Scatter |
|
A scatter plot (points not joined) chart that allows the charting of 2 related attribute series. Can only be used if the data series are related. Useful for seeing trends in data that is not linear. |
Histogram |
|
Shows the number of times a given value occurs in the dataset. |
Box & Whisker |
|
A chart which gives a quick overview of series of values and their statistical properties. |
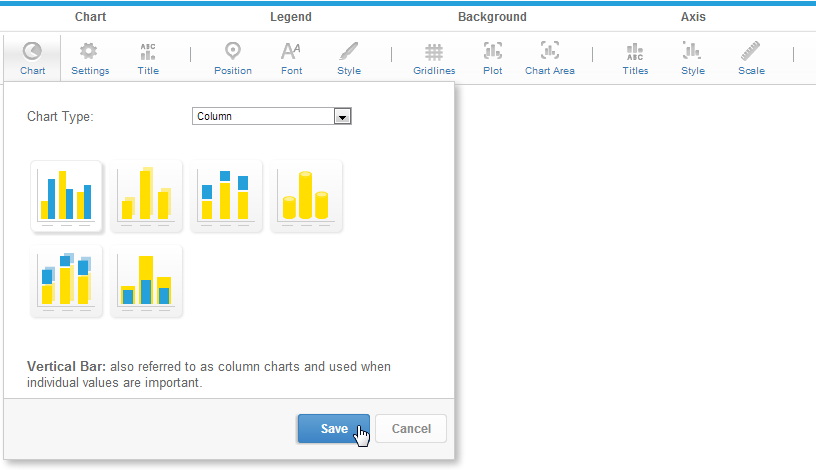
Chart Selector